git - Version control#
1. What is git?#
For a short explanation of the concept of git, watch the video “What is Git? Explained in 2 Minutes!”
git is a Version Control System#
A Version Control System is a software that tracks the file changes of all contributors within a project.
Originally developed to assist collaborative open source software development by Linus Torvalds (Initiator of Linux development)
The user chooses which files are tracked and which file changes are recorded.
All tracked files of a project are stored in a git repository (“repo”).
git tracks file changes through commits#

git log shows all commits of this repository#
$ git log
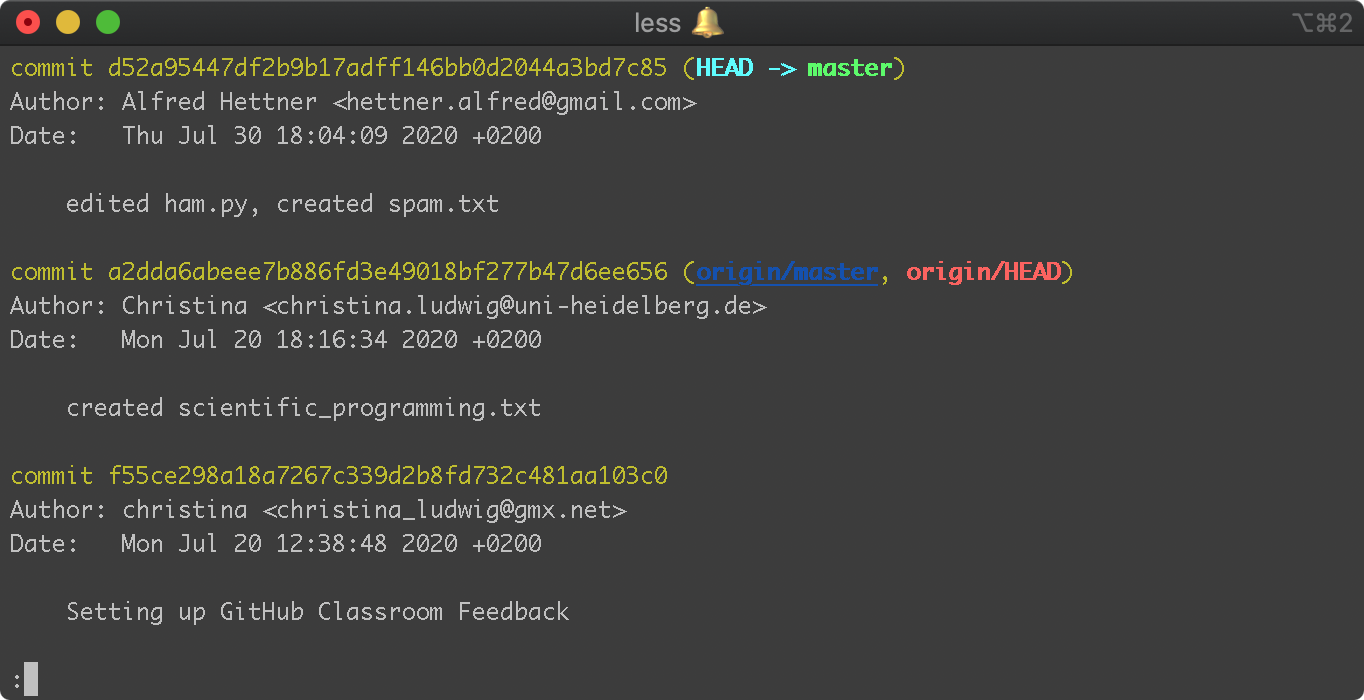
Note: You can exit the log by typing “q”, if you use the default command line editor vim.
git status shows the current state of the repository#
$ git status
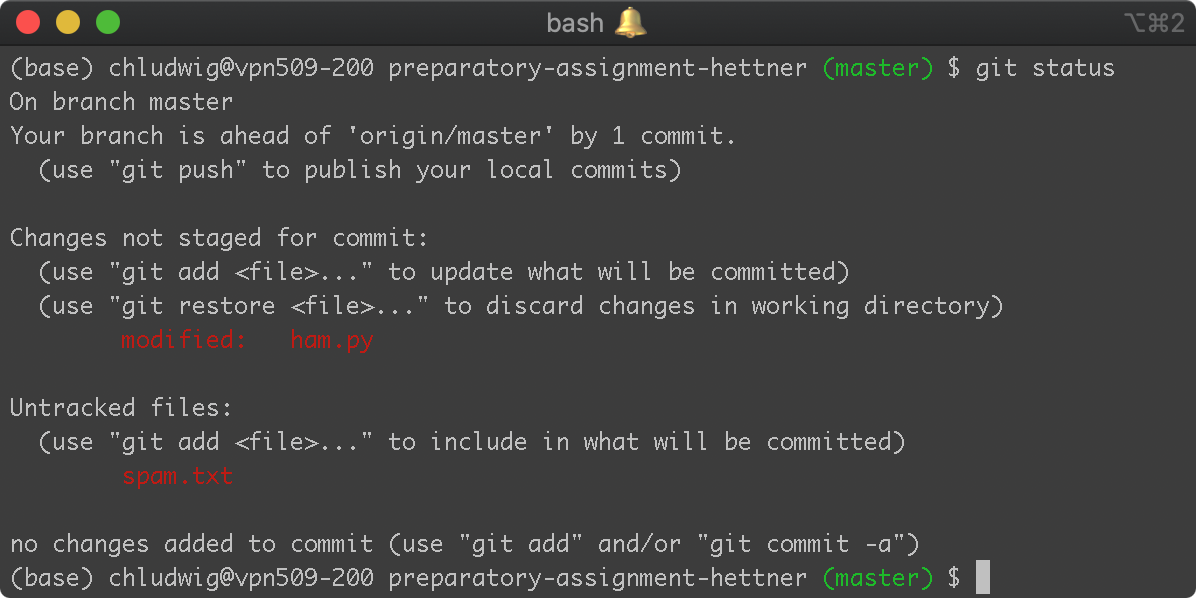
A commit records file changes within the repository#
Adding new or edited files to the staging area, which will be included in the next commit.
$ git add ham.py
$ git add spam.txt
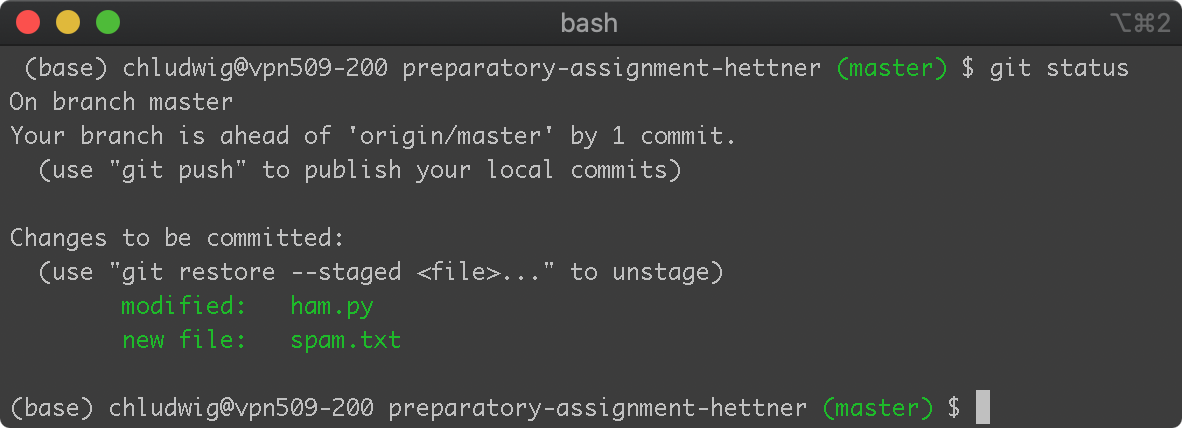
Creating the commit containing the files in the staging area:
$ git commit -m "edited ham.py, created spam.txt"
Video Tutorial: Click on the image below to watch a video tutorial on how to create a commit. Note that the files and the URLs in the video will be different from yours but the principle is the same..
For a more extensive git tutorial watch the video Git Tutorial for Beginners: Learn Git in 1 Hour.
git needs to know who is creating the commit#
Registering your user name and email:
$ git config --global user.name "Alfred Hettner"
$ git config --global user.email "hettner.alfred@gmail.com"
Note: This has to be done only once. It does not have to be your GitHub user name or email.
Synchronizing your local commits with a central git repository#
Connecting a local repository to a central repository#
Option 1: Clone the repository to your computer:
$ git clone https://github.com/geoscripting/preparatory-assignment-hettner
Video Tutorial: Click on the image below to watch a video tutorial on how to clone a repository. Note that the files and the URLs in the video will be different from yours but the principle is the same.
Option 2: Create a local repository and connect it to a central repository:
$ git init
$ git remote add origin https://github.com/hettner/my_empty_repo.git


